| 알파스팀(Alpha-Stim)에 대해서 | 목록으로 가기 |
섬유근육통과 관련된 통증에 대한 뇌 전기 요법 자극(CES)의 효과
date: 2022.05.04
Cork, Randall C., Wood, Patrick, Ming, Norbert, Shepherd, Clifton, Eddy, James, Price, Larry. 섬유 근육통과 관련된 통증에 대한 뇌 전기 요법 자극(CES)의 효과. 마취의 인터넷 저널. 2004년; 8(2).
장치
알파 스팀(Alpha-Stim)®
주요 변수
불안감
목적
포함 및 제외 기준을 충족하는 피험자에서 동일한 실험 조건에서 가짜 치료와 비교할 때 섬유근육통 환자의 불안, 통증, 압통점 점수 및 기능 손상에 대한 CES를 사용한 특정 치료 과정의 효과를 평가합니다. 불안의 변수에 대한 발견은 이 초록에서 논의됩니다.
테스트 설계
IRB에서 승인한 6주 연구에는 3주간의 무작위 배정된 가짜 치료 대조 임상 시험군이 포함된 후 가짜 그룹의 피험자가 CES 치료 과정에 참여하는 3주간의 공개 라벨이 있는 군이 포함되었습니다. 연구자들은 이 연구를 위해 Alpha-Stim 이중 맹검, 가짜 대조 RCT 프로토콜을 사용했습니다.
1차 유효성 결과: 불안감
1상 RCT에서 불안에 대한 1차 유효성 평가변수는 연구 3주차 말에 가짜 치료 그룹과 비교하여 기분 상태 프로파일(POMS)에 대한 마지막 치료 후 점수의 기준선으로부터의 변화였습니다. 2상 공개 라벨 부문에서 불안에 대한 1차 유효성 평가변수는 연구 6주가 끝날 때 POMS에 대한 마지막 치료 후 점수의 기준선에서 사후 테스트로의 변화였습니다.
기타 효과성 결과 측정은 연구 3주차 말에 측정되었으며 임상의가 평가한 결과 측정과 환자가 평가한 결과 측정을 모두 포함했습니다. 다음 임상의 평가 측정이 포함되었습니다. 압통 점수 평가. 다음과 같은 환자 평가 측정이 포함되었습니다: McGill 통증 설문지(SF-MPQ) 및 통증으로 인한 기능 손상에 대한 Oswestry 점수.
주요 포함 기준
• 22~75세 범위의 섬유근육통이 있는 남성 및 여성 피험자.
• 섬유근육통 진단은 섬유근육통 분류를 위한 미국 류마티스학회 기준(Wolfe et al., 1990)의 기준을 사용하여 의사의 통증 전문가에 의해 확인되었습니다.
• 섬유근육통 진단은 섬유근육통 분류를 위한 미국 류마티스학회 기준(Wolfe et al., 1990)의 기준을 사용하여 의사의 통증 전문가에 의해 확인되었습니다.
주요 제외 기준
• 임신.
• 이식된 심박조율기, 펌프 또는 자극기의 존재.
• 표재성 또는 내부 귀 감염.
• 이식된 심박조율기, 펌프 또는 자극기의 존재.
• 표재성 또는 내부 귀 감염.
프로토콜 요약
무작위 배정은 Alpha-Stim® CES 장치 제조업체가 연구 시작 전에 설정했습니다. 1차 유효성 평가변수 및 2차 결과 측정값에 대한 평가는 치료 기간 시작 전 기준선에서 수행되었습니다. 연구 기간 동안 환자의 의학적 관리에는 변화가 없었습니다. 프로토콜은 2단계로 구성되었습니다.
• 1단계: 활성 CES 장치 또는 가짜 장치로 3주 치료.
베이스라인 테스트 후, 피험자들은 CES 장치를 사용하도록 교육받았고, 3주 동안 매일 1시간 동안 사용하도록 지시받았습니다. 3주가 끝날 때 피험자들은 진료소로 돌아왔고 1차 및 2차 결과 측정을 반복했습니다.
• 2단계: 눈가림이 해제된 후 가짜 그룹의 피험자들에게 3주 동안 활성 CES를 받을 수 있는 옵션이 주어졌습니다. 그렇게 하기로 선택한 사람들은 3주 기간 후에 클리닉에 돌아와 재검사를 받았습니다.
베이스라인 테스트 후, 피험자들은 CES 장치를 사용하도록 교육받았고, 3주 동안 매일 1시간 동안 사용하도록 지시받았습니다. 3주가 끝날 때 피험자들은 진료소로 돌아왔고 1차 및 2차 결과 측정을 반복했습니다.
• 2단계: 눈가림이 해제된 후 가짜 그룹의 피험자들에게 3주 동안 활성 CES를 받을 수 있는 옵션이 주어졌습니다. 그렇게 하기로 선택한 사람들은 3주 기간 후에 클리닉에 돌아와 재검사를 받았습니다.
장치 응용 프로그램 요약
활성 CES 장치는 제조사에서 사전 설정하고 하위 감각 수준인 100μA로 잠갔습니다. 가짜 CES 장치는 전기를 방출하지 않도록 제조업체에서 미리 설정하고 잠갔습니다. 치료 기간인 60분도 활성 장치와 가짜 장치 모두에 대해 제조업체에서 미리 설정하고 잠그었습니다. 가짜 장치는 활성 CES 장치와 모양이 동일했지만 전류를 전도하지 않았습니다. 장치는 제조업체에서 무작위로 추출한 다음 피험자에게 제공되어야 하는 순서대로 장치 상자에 포장했습니다.
스터디 블라인드
피험자, 조사자, 의사 및 직원은 모두 장치의 ID로 마스킹되었습니다.
산출측정지표
기분 상태 프로파일(POMS)은 불안을 측정하는 데 사용되었습니다. POMS는 신뢰성과 타당성을 확립했습니다(McNair et al., 2014).
결과
피험자
총 74명의 피험자가 등록되었으며, 70명의 여성과 4명의 남성이 22~75세(남성 = 53세)의 연령대였습니다. 증상의 평균 지속 기간은 7.3년(범위 1-21년)이었습니다. 피험자들은 활성 CES 그룹(N=39) 또는 가짜 그룹(N=35)으로 무작위 배정되었습니다.
기준 측정
모든 결과 측정에 대해 활성 CES와 가짜 치료 그룹 간에 기준선에서 통계적으로 유의한 차이가 없었습니다.
데이터 분석
데이터는 연구의 1상과 2상 모두에서 사후 테스트에서 가장 큰 차이가 없는 반복 측정 분산 분석으로 분석되었습니다.
1상 RCT 효과 결과: 3주차
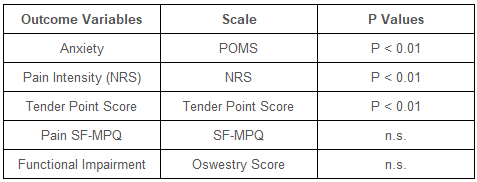
74명의 피험자, 39명의 활성 CES 및 35명의 Sham이 3주차 방문 완료 시 테스트를 완료했습니다. 활동적인 CES 그룹은 가짜 그룹에 비해 불안 점수, 압통점 및 통증이 유의하게 감소했습니다. McGill Pain Questionnaire로 측정한 통증이나 기능 장애에 대해서는 그룹 간에 유의한 차이가 없었습니다. Table 1은 모든 결과 측정의 통계적 분석 결과를 보여준다.
 |
2상 공개 라벨 효과 결과: 6주
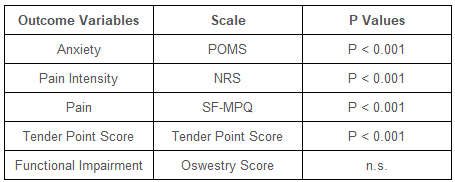
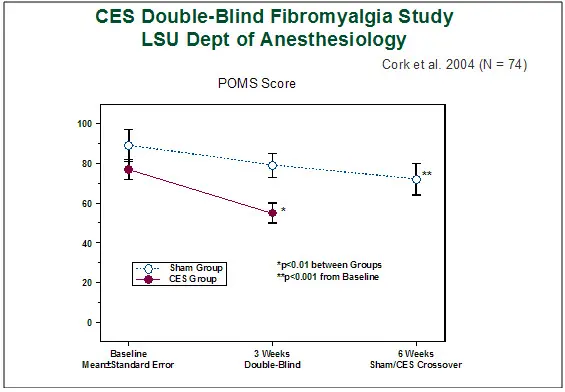
데이터는 최소 유의차 사후 테스트와 함께 분산의 반복 측정 분석으로 분석되었습니다. 표 2는 6주차의 결과 측정에 대한 통계적 분석 결과를 보여줍니다. 그림 1은 POMS로 측정한 환자의 기분을 보여줍니다. 여기서 점수가 높을수록 불안이 더 많이 나타납니다.
 |
 |
연구의 가치
이 연구의 강점은 다음과 같습니다. 이중 맹검, 가짜 통제 RCT 설계의 사용; 활성 및 가짜 장치는 시간 및 전류 수준에 대해 사전 설정되었으며 가짜 CES 장치는 전기를 방출하지 않는다는 점을 제외하고 활성 CES 장치와 동일했습니다. 이 연구는 불안 치료를 위한 CES의 효과 크기에 대한 연구를 기반으로 N이 74로 적절하게 검증되었습니다. 이 2004년 연구는 당시 일반적으로 사용된 POMS 척도를 사용하여 일반 불안을 측정했으며 문헌에서 임상 및 연구 효용성을 확립했습니다. 오늘날 조사자들이 선택할 가능성이 더 높은 것은 Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale 또는 기타 유사한 불안 척도입니다. 이 연구에서 불안에 대한 중요한 발견은 CES가 불안을 유의하게 감소시킨다는 다른 CES RCT의 발견과 일치합니다.
저자 소속
RCC, 교수 겸 의장 책임자, 통증 관리, 마취과
LSUHSC, LA 슈리브포트에 있는 루이지애나 주립대학교 의과대학.
LSUHSC, LA 슈리브포트에 있는 루이지애나 주립대학교 의과대학.
참고문헌
McNair DM, Lorr M, Droppleman LF. Mood States 2nd Edition(POMS 2™) 프로필. JvR Psychometrics, 2014년 4월 18일에 액세스, http://www.psychologyafrica.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/Profile_of_Mood_States_2nd_Edition.pdf
Wolfe, et al. 미국 류마티스학회 섬유근육통 분류 기준: 다기관 기준 위원회 보고서. 관절염 Rheum, 33:160-172, 1990.
Wolfe, et al. 미국 류마티스학회 섬유근육통 분류 기준: 다기관 기준 위원회 보고서. 관절염 Rheum, 33:160-172, 1990.
원문보기
The effect of cranial electrotherapy stimulation (CES) on pain associated with fibromyalgia
Cork, Randall C., Wood, Patrick, Ming, Norbert, Shepherd, Clifton, Eddy, James, Price, Larry. The effect of cranial electrotherapy stimulation (CES) on pain associated with fibromyalgia. The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology. 2004; 8(2).
Device
Alpha-Stim®
Key Variable
Anxiety
Objective
To evaluate the effect of a specified treatment course with CES on fibromyalgia patients’ anxiety, pain, tender point scores, and functional impairment when compared to sham treatment under the same experimental conditions in subjects meeting the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The findings for the variable of anxiety are discussed in this abstract.
Design
An IRB approved 6 week study that included a 3 week randomized, sham treatment controlled clinical trial arm followed by a 3-week open label arm in which subjects in the sham group participated in a treatment course of CES. The investigators used the Alpha-Stim double-blind, sham-controlled RCT protocol for this study.
Primary Effectiveness Endpoint: Anxiety
The primary effectiveness endpoint for anxiety in the Phase I RCT was the change from baseline in the last post-treatment scores on the Profile of Mood States (POMS) compared to the sham treatment group at the end of week 3 of the study. The primary effectiveness endpoint for anxiety in the Phase II open label arm was the change from baseline in the last post-treatment scores on the POMS to post-test at the end of week 6 of the study.
Other effectiveness outcome measures were measured at the end of week 3 of the study and included both clinician rated and patient rated outcome measures. The following clinician rated measures was included: Tender point score evaluation. The following patient rated measures were included: McGill Pain Questionnaire (SF-MPQ), and Oswestry Score for functional impairment from pain.
Key Inclusion Criteria
• Male and female subjects with fibromyalgia ranging from 22 – 75 years of age.
• Diagnosis of fibromyalgia was verified by a physician pain specialist using the criteria of the American College of Rheumatology Criteria for the Classification of Fibromyalgia (Wolfe et al., 1990).
• Diagnosis of fibromyalgia was verified by a physician pain specialist using the criteria of the American College of Rheumatology Criteria for the Classification of Fibromyalgia (Wolfe et al., 1990).
Key Exclusion Criteria
• Pregnancy.
• Presence of implanted pacemakers, pumps or stimulators.
• Superficial or internal ear infections.
• Presence of implanted pacemakers, pumps or stimulators.
• Superficial or internal ear infections.
Protocol Summary
Randomization assignment was established prior to the start of the study by the manufacturer of Alpha-Stim® CES devices. Evaluations of primary effectiveness endpoint and secondary outcome measures were taken at baseline prior to the start of the treatment period. No change was made in the medical management of the patients during the study. The protocol consisted of 2 phases:
• Phase I: 3 weeks of treatment with either the active CES device or the sham device.
Following the baseline tests, subjects were taught to use the CES device, and were instructed to use it every day for 1 hour over the 3 week period. At the end of 3 weeks, the subjects returned to the clinic, and primary and secondary outcome measures were repeated.
• Phase II: After the blinding was broken subjects in the sham group were given the option to receive active CES for 3 weeks. Those that elected to do so returned to the clinic after the 3 week period and were retested.
Following the baseline tests, subjects were taught to use the CES device, and were instructed to use it every day for 1 hour over the 3 week period. At the end of 3 weeks, the subjects returned to the clinic, and primary and secondary outcome measures were repeated.
• Phase II: After the blinding was broken subjects in the sham group were given the option to receive active CES for 3 weeks. Those that elected to do so returned to the clinic after the 3 week period and were retested.
Device Application Summary
The active CES device was pre-set and locked by the manufacturer at 100 µA which is a subsensory level. The sham CES device was pre-set and locked by the manufacturer so that it did not emit electricity. The length of treatment, 60 minutes, was also pre-set and locked by the manufacturer for both active and sham devices. The sham device was identical in appearance to the active CES unit, but did not conduct an electrical current. The devices were randomized by the manufacturer and then packed in a device box in the order they should be given to subjects.
Study Blinding
The subjects, investigators, physicians and staff were all masked to the identity of the devices
Outcome Measures
The Profile of Mood States (POMS) was used to measure anxiety. The POMS has established reliability and validity (McNair et al., 2014).
Results
Subjects
A total of 74 subjects were enrolled, 70 females and 4 men ranging in age from 22 – 75 (M = 53) years of age. The average duration of symptoms was 7.3 years (range 1 -21 years). Subjects were randomized to the active CES group (N=39) or sham group (N=35).
Baseline Measurements
There were no statistically significant differences at baseline between active CES and sham treatment groups for any of the outcome measures.
Data Analysis
Data were analyzed with repeated measures analysis of variance, with least significant difference a posteriori testing in both Phase I and Phase II of the study.
Phase I RCT Effectiveness Results: Week 3
Seventy-four (74) subjects, 39 active CES and 35 Sham, completed the testing at the completion of week 3 visit. The active CES group had significantly decreased anxiety scores, tender points and pain compared to sham group. There was no significant difference between groups on pain as measured by the McGill Pain Questionnaire, or functional impairment. Table 1 shows results of statistical analyses of all outcome measures.
 |
Phase II Open Label Effectiveness Results: 6 Weeks
Data were analyzed with repeated measures analysis of variance, with least significant difference a posteriori testing. Table 2 shows results of statistical analyses of outcome measures at week 6. Figure 1 shows patient mood as measured by the POMS where higher scores represent more anxiety.
 |
 |
Quality of the Research
Strength of this study are; use of a double-blind, sham controlled RCT design; the active and sham devices were preset for time and current level, and the sham CES device was identical to the active CES device except they did not emit electricity; the study was adequately powered with an N of 74, based on the research on the effect sizes for CES for treatment of anxiety. This 2004 study measured general anxiety using the POMS scale which was commonly used at that time and has established clinical and research utility in the literature. Today, a more likely choice by investigators would be the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale or other similar anxiety scale. The significant finding for anxiety in this study is consistent with findings from other CES RCTs that showed CES significantly decreases anxiety.
Author Affiliation
RCC, Professor and Chair Director, Pain Management, Department of Anesthesiology
Louisiana State University School of Medicine in Shreveport, LSUHSC, LA.
Louisiana State University School of Medicine in Shreveport, LSUHSC, LA.
References
McNair DM, Lorr M, Droppleman LF. Profile of Mood States 2nd Editon (POMS 2™). JvR Psychometrics, Accessed on 4/18/2014, http://www.psychologyafrica.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/Profile_of_Mood_States_2nd_Edition.pdf
Wolfe, et al. American College of Rheumatology Criteria for the Classification of Fibromyalgia: Report of the Multicenter Criteria Committee. Arthritis Rheum, 33:160-172, 1990.
Wolfe, et al. American College of Rheumatology Criteria for the Classification of Fibromyalgia: Report of the Multicenter Criteria Committee. Arthritis Rheum, 33:160-172, 1990.
출처: 알파스팀제조사 EPI 홈페이지
| 목록으로 가기 |





